Introduction:
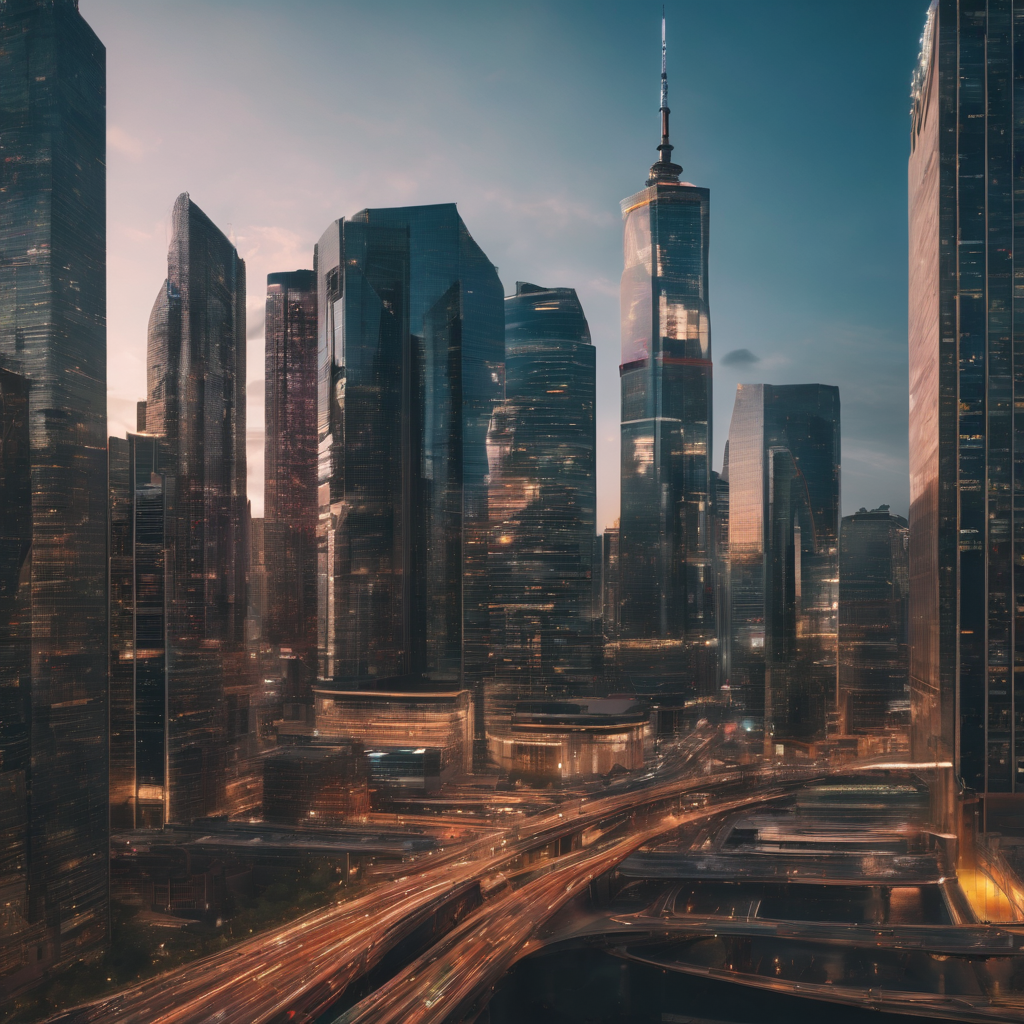
In an era marked by rapid urbanization, the concept of smart cities has emerged as a beacon of innovation, promising to enhance the quality of life for residents while promoting sustainable development. Smart cities leverage cutting-edge technologies to optimize urban infrastructure, streamline services, and foster a more efficient, connected, and environmentally conscious urban landscape.
Foundational Technologies:
Internet of Things (IoT)
At the core of smart city solutions lies the Internet of Things (IoT), a network of interconnected devices that collect and share data in real-time. In smart cities, IoT-enabled sensors and devices are strategically deployed throughout the urban environment to monitor and manage various aspects, such as traffic flow, energy consumption, and waste management.
Big Data Analytics
The data generated by IoT devices is a goldmine of information. Big data analytics processes this vast amount of data to extract valuable insights. In smart cities, this technology is applied to optimize resource allocation, improve traffic management, and enhance public services based on data-driven decision-making.
Key Applications
Smart cities address the challenges of urban mobility through intelligent transportation systems. Real-time traffic monitoring, smart parking solutions, and advanced public transportation systems help reduce congestion, lower emissions, and enhance overall transportation efficiency.
Efficient energy use is a cornerstone of smart cities. Smart grids and energy management systems enable cities to monitor, control, and optimize energy consumption, promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact.
From smart buildings to connected utilities, the integration of technology into infrastructure enhances the overall functionality of cities. Automated systems for water supply, waste management, and public safety contribute to a more resilient and responsive urban environment.
Connectivity and Communication
a. 5G Technology:
The advent of 5G technology plays a pivotal role in the development of smart cities. With its high-speed, low-latency capabilities, 5G enhances connectivity, enabling real-time communication between devices and systems. This facilitates the seamless operation of various smart city applications.
b. Smart Governance and Citizen Engagement:
Technology empowers citizens by providing them with platforms for participation in decision-making processes. Smart city initiatives often include digital interfaces for citizens to access services, report issues, and engage with local government, fostering a more inclusive and responsive urban governance model.
Challenges and Considerations
a. Privacy and Security:
As smart cities rely heavily on data collection and sharing, ensuring the privacy and security of citizens’ information is paramount. Robust cybersecurity measures and ethical data practices are essential to build and maintain public trust.
b. Integration and Standardization:
The integration of diverse technologies and the establishment of standardized protocols are crucial for the seamless operation of smart city solutions. Collaboration among stakeholders, including government bodies, private enterprises, and citizens, is necessary to create a cohesive and interoperable urban ecosystem.
Conclusion
Smart cities represent a paradigm shift in urban development, leveraging technology to create more efficient, sustainable, and livable environments. As cities continue to grow, embracing smart city solutions becomes not only a necessity but also a beacon of hope for a future where technology harmoniously coexists with urban life, creating a positive impact on the well-being of citizens and the planet.